Mycotoxin and Shell Fish Toxin
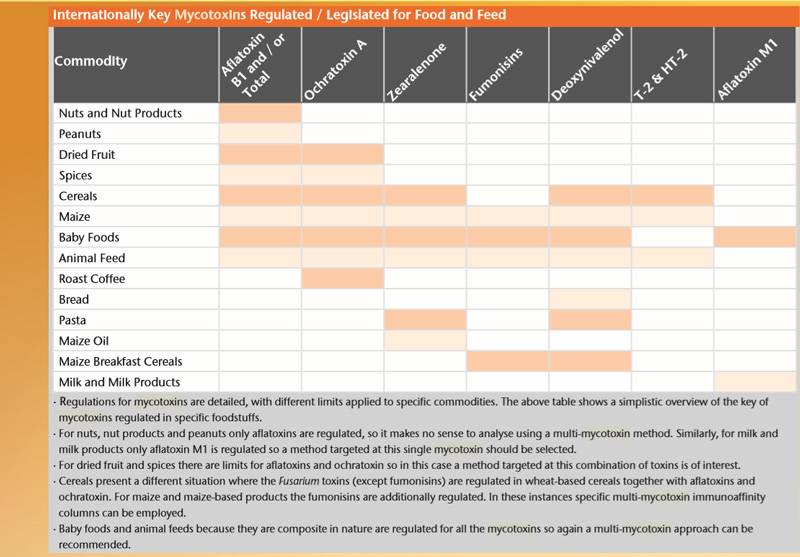
Mycotoxin are toxic metabolites produced by some molds and fungi and have serious acute effects on humans and husbandry animals. There are several hundred mycotoxins known but those that concern human health and livestock include aflatoxin, ochratoxin A, patulin, fumonisin, zearalenone, nevalenol/deoxynivalenol.Exposure to mycotoxins can happen either directly by eating infected food or indirectly from animals that are fed contaminated feed, in particular from milk. International standards and code of practice for mycotoxins are established by Codex Alimentarius.
In the EU, the standards for mycotoxin are listed in the Commission Regulation EC No 1881/2006
In Singapore, the maximum residue limit for mycotoxin is stated in the Singapore Food Regulation.
Shell Fish Toxin
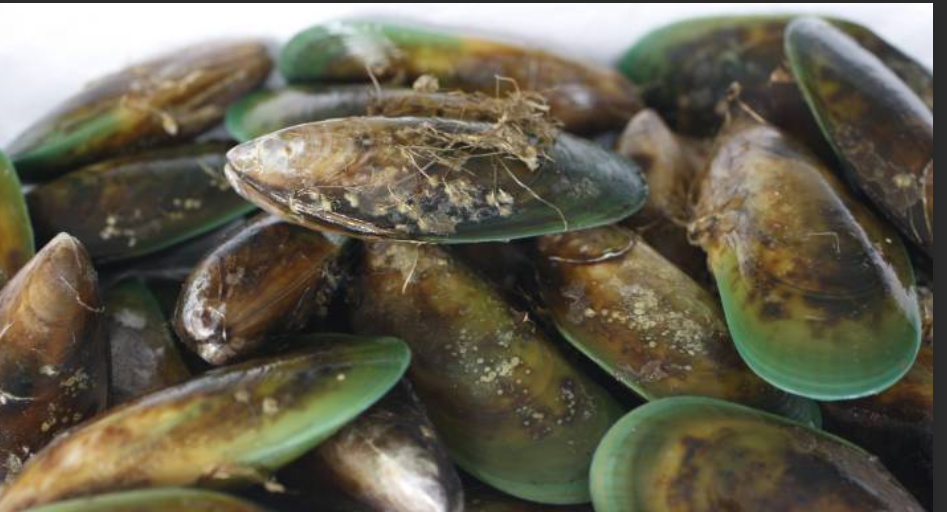


High concentrations of shell fish toxins can accumulate in many marine filter feeders such as clams, mussels and oysters. There are four syndromes that are usually caused by shell fish poisoning i.e. paralytic shell fish poisoning (PSP), diarrhetic shell fish poisoning (DSP), neurotic shell fish poisoning (NSP), and amnesic shell fish poisoning (ASP). The polyether toxins, okadiac acid and its analogues dinophysistoxin DTX1, DTX2, DTX3 causes DSP. The EU Regulation EC 853/2004 states that live mollusks must not contain okadiac acid and/or its equivalents like dinophysistoxin and pectenotoxin, of more than 160µg per kilo. The EU regulation (EC) no 853/2004 states that mollusks must contain PSP toxins (saxitoxin and its analogues) of not more than 800µg per kg.
In the European Union, EU Regulation EC 853/2004 stipulates that live bivalve mollusks must not contain PSP toxins (saxitoxin and analogues) in total quantity (measured in the whole body or any part edible separately) that exceeds a limit of 800μg per kilogram.
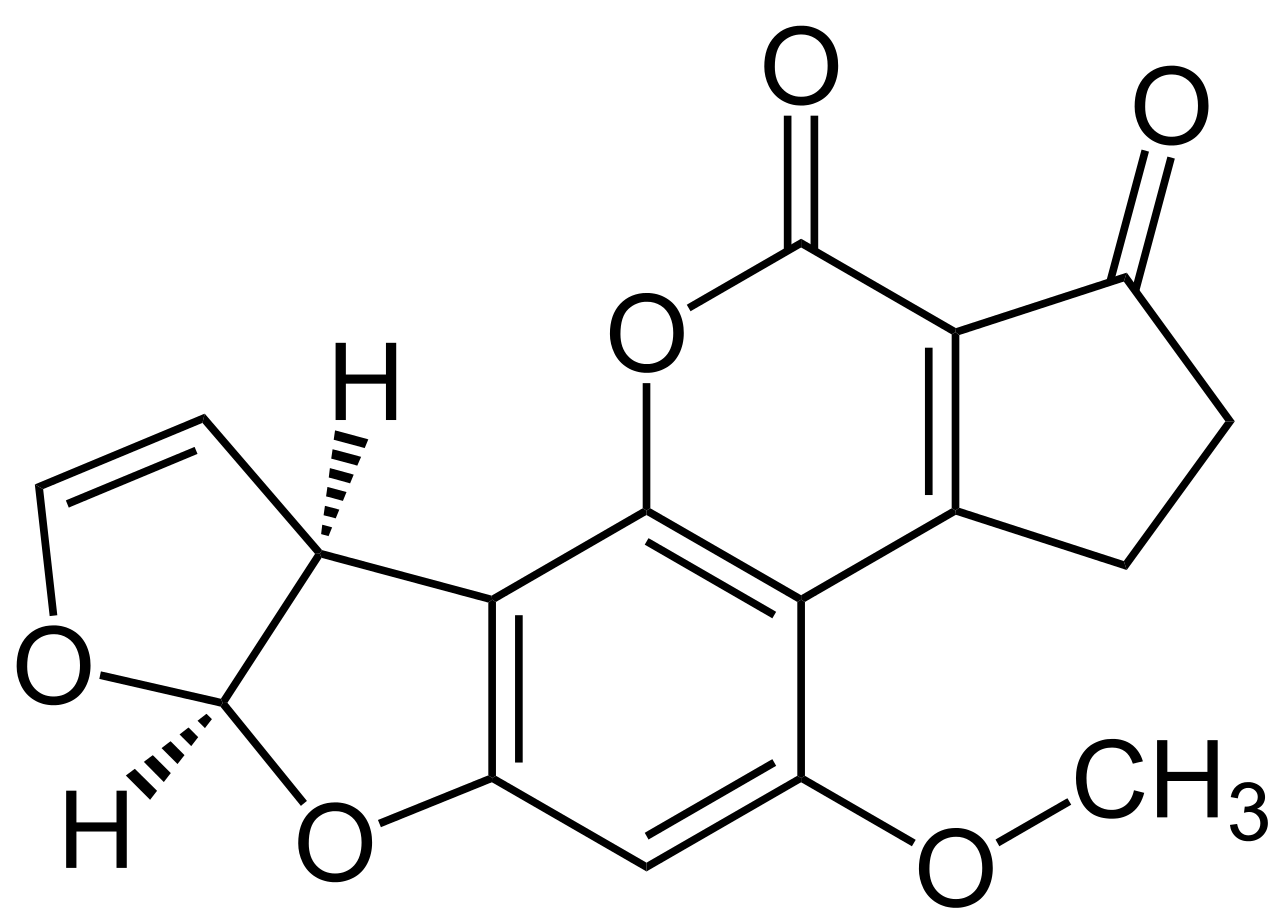
Aflatoxin
Aflatoxin are amongst the most poisonous mycotoxin and they are produced by molds e.g. aspergillus flavus and A. parasiticus which grow in soil and decaying vegetation and crops like corn, peanuts, spices, oilseeds and tree nuts. They can also be found in milk that are produced from animals fed with these toxin. Large doses can lead to acute poisoning, damage DNA and cause cancer especially liver cancer in humans.
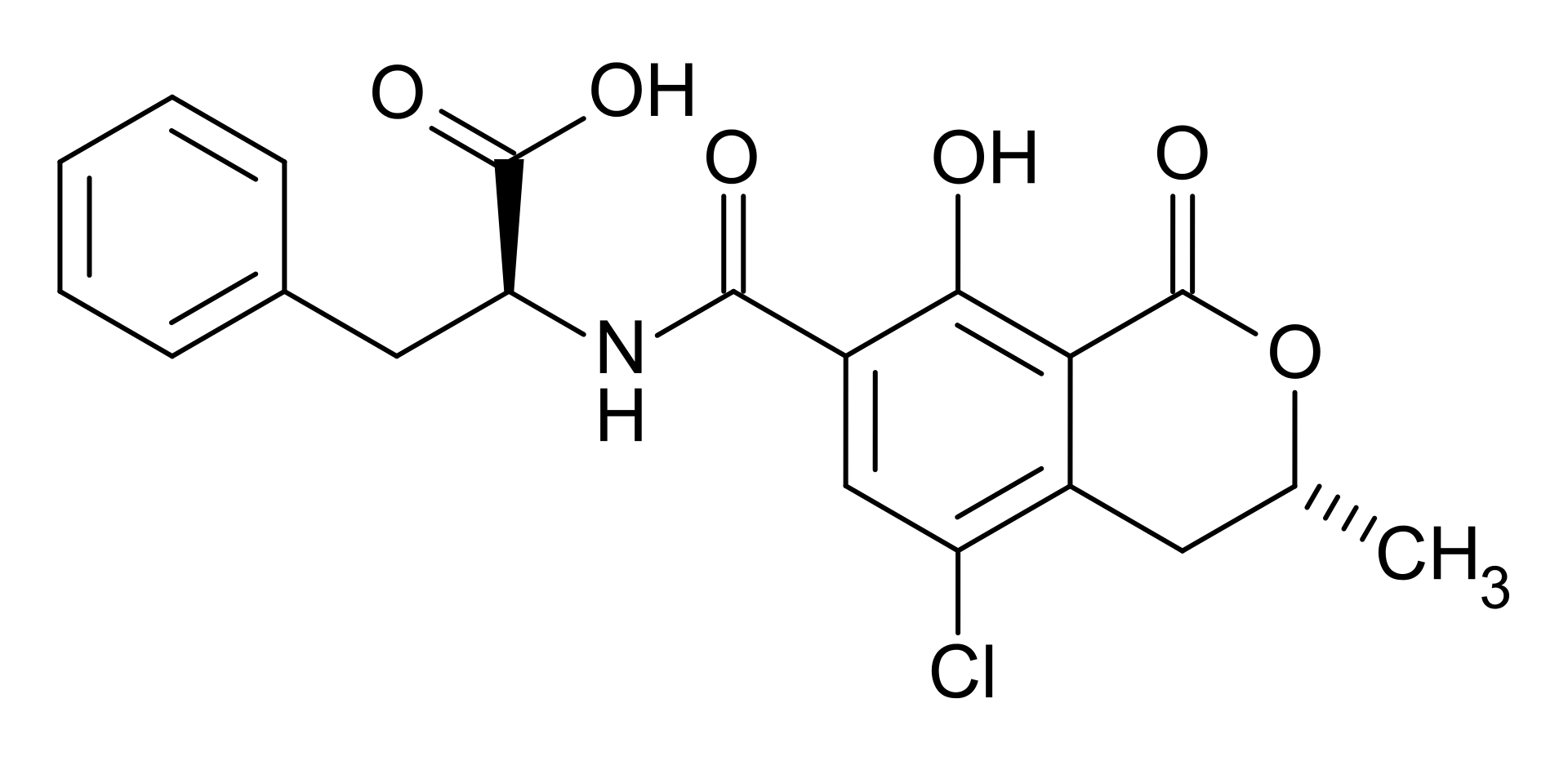
Ochratoxin
Ochratoxin is produced by some species of aspergillus and penicillium. Commonly contaminated foods are cereals, wine, coffee, dry vine fruits, grape juice, spices and liquorice. This toxin can cause kidney damage, cancer, fetal development, and damage the immune system.
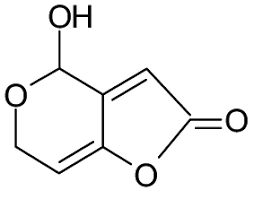
Patulin
Patulin is produced by molds such as aspergillus, penicilium and byssochlamys. They are commonly found in apples, moldy fruits, grains and other foods. They cause liver, kidney, spleen and damage the immune system.
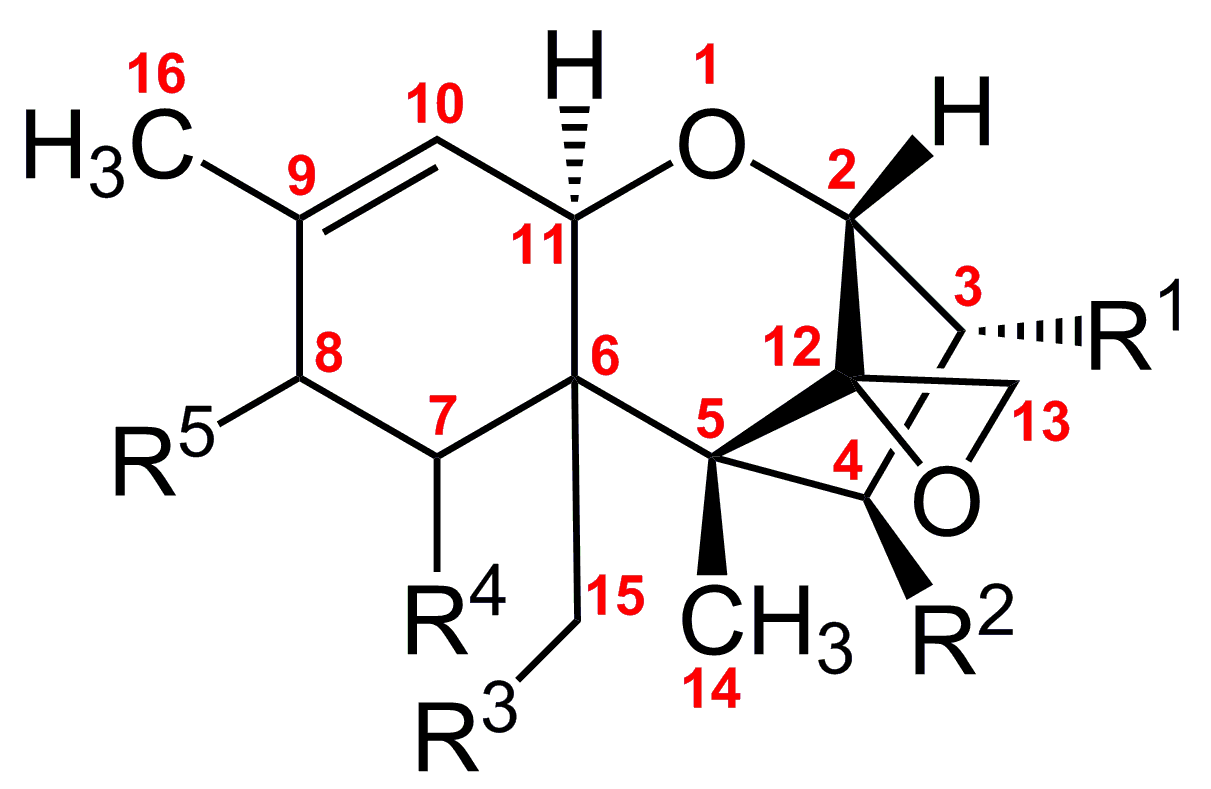
Trichothecenes (Fusarium Fungi)
Fusarium fungi produces a range of toxin in the class trichothecenes such as deoxynivalenol (DON), nevalenol (NIV), T-2 and HT-2 toxins, as well as zearalenone (ZEN) and fumonisins. DON and ZEN are often associated with wheat, T-2 and HT-2 toxins with oats, and fumonisins with maize (corn). Trichothecenes can be acutely toxic to humans, causing rapid irritation to the skin or intestinal mucosa and lead to diarrhea. Reported chronic effects in animals include suppression of the immune system. ZEN has been shown to have hormonal, estrogenic effects and can cause infertility at high intake levels, particularly in pigs. Fumonisins have been related to esophageal cancer in humans, and to liver and kidney toxicity in animals.
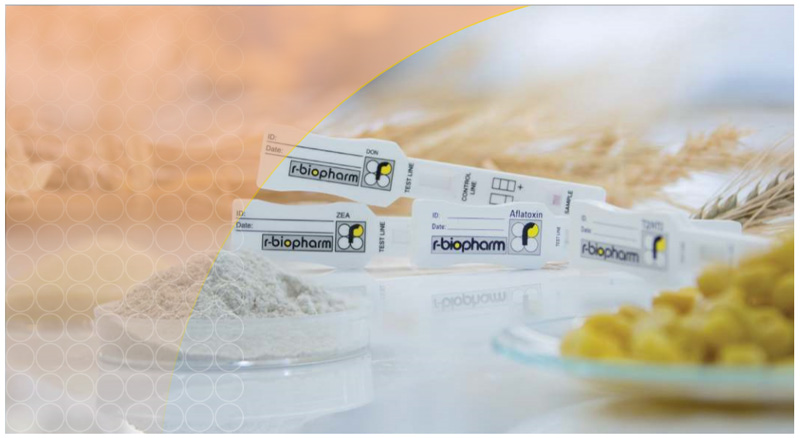
Test Method for Mycotoxin

We provide the best services about science.
About Company
Sitemap
Please contact our friendly sales staff for more information.
Feel free to ask us questions. We would love to assist you !