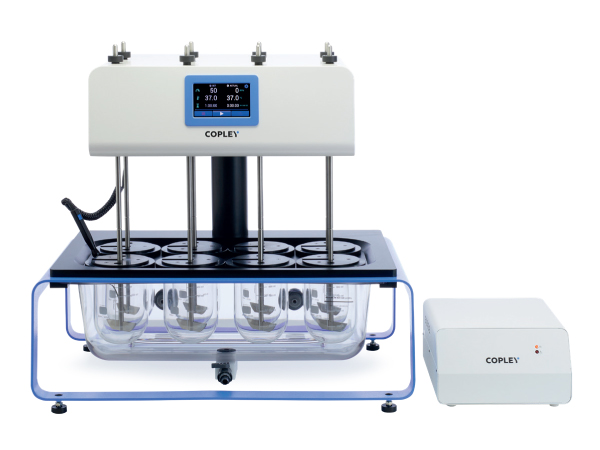
Dissolution Testing
Optimising the amount of a drug available to the body following administration, i.e. its bioavailability, remains one of the greatest challenges the pharmaceutical industry faces. Inadequacies in bioavailability can mean a treatment is ineffective or even potentially dangerous (e.g. overdose).
The progressive optimisation of dissolution testing for different pharmaceutical forms has led to the introduction of a range of different apparatuses and techniques as detailed in Ph. Eur Chapters 2.9.3, 2.9.4 and USP Chapters <711> and <724>.
Determining bioavailability via in vivo drug release analysis studies (e.g. urine or plasma analysis) can be impractical, particularly when such techniques are required on a routine basis. To overcome such issues, official in vitro dissolution tests have been rigorously and comprehensively defined in the respective Pharmacopoeias and are essential for:
- Predicting in vivo drug bioavailability.
- Assessing bioequivalence and its application in scale-up and post-approval changes.
- Optimising therapeutic effectiveness during development and stability assessment.
- Ensuring uniformity between production lots.
The most commonly used apparatus defined by the Pharmacopoeias to measure the dissolution rate of solid dose forms are the basket and paddle. The basic dissolution apparatus consists of a covered cylindrical vessel with a hemispherical bottom, typically holding 1000 mL of simulated gastric juice. The vessel is immersed in a water bath capable of maintaining the temperature of the vessel contents at 37 °C. For the basket method, the tablet or capsule is constrained in a cylindrical basket, constructed of sieve mesh, of defined proportions. The basket is attached to a metal drive shaft, positioned so that the bottom of the basket is 25 mm from the bottom of the vessel. Samples of the dissolution medium are taken at predefined time intervals to determine the percentage of dissolved drug present – typically using a UV/Vis Spectrophotometer or high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC).