Food Safety - Staphylococcus

Food Safety
Staphylococcus
Testing for Staphylococcus in Food Industries
Staphylococcus are present in the environment and can be found on the skin and upper respiratory tract. Pathogenic species include S. aureus, S. epidermidis, S. saprophyticus, S. intermedius, S. pseudintermedius. The bacteria can mutate and a strain of S. aureus was found to be resistant to the drug methicillin and it is labelled as MRSA. In 1997, a strain of S. aureus was isolated as resistant to vancomycin. Staph aureus is also the cause of mastitis in sheep and cow udders. S. aureus has a high salt tolerance and grow in ham, meat, dairy products, sandwiches, cream filled pastries, chocolates and cold salads. As such it is important to test for this bacteria in ready to eat foods and chocolate. Staph aureus can survive in a dry state but outbreaks are usually due to post processing contamination and or thermal abuse. They have an amazing ability to form biofilms.
Staphylococcus is a spherical non- sporulating, non-motile bacteria and usually occurs in pairs, short chains and grape like clusters. They belong to the family Staphylococcaceae. They are facultative aero anaerobic and are gram positive and catalase positive. S aureus produces an array of toxin that are not destroyed by heat. Some of the toxins are cytolytic and some hemolysins e.g. alpha, beta and delta toxins. They also produce a wide array of enterotoxin and enterolike toxins and emetic toxins. Toxins are usually produced by coagulase positive Staph and seldom by coagulase negative Staph. Existing testing methods do not detect all staph toxins due to its differences.
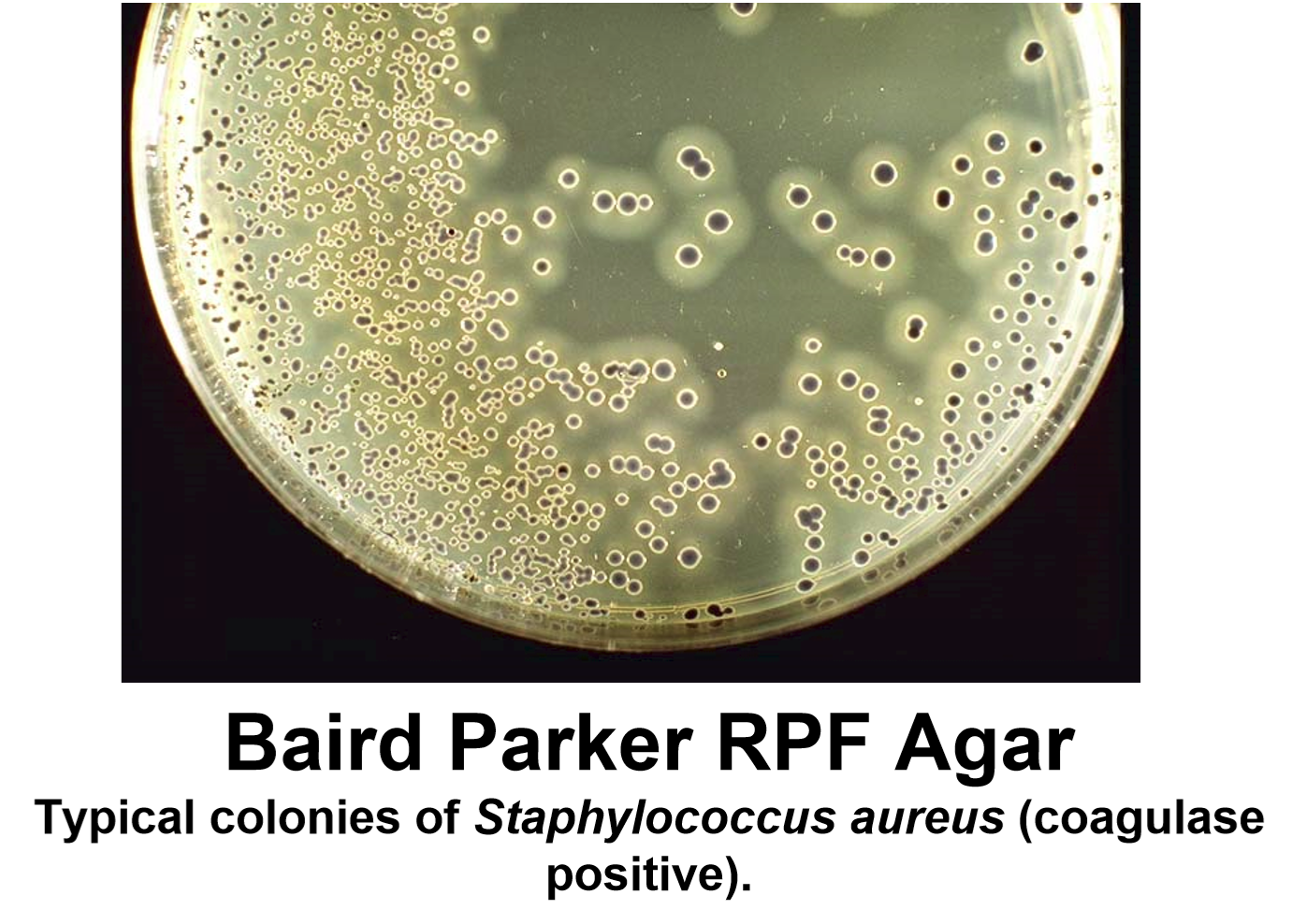
Biolife Baird Parker Agar is a selective medium recommended by USP and EP for isolation of S aureus in non-sterile pharmaceutical products. Lithium chloride and potassium tellurite inhibit contaminating flora and glycine and sodium pyruvate facilitate the development of staphylococci. Some yeasts, fungi and bacilli will also grow, but these are easily distinguishable by their morphology and by the grey color of the colonies.
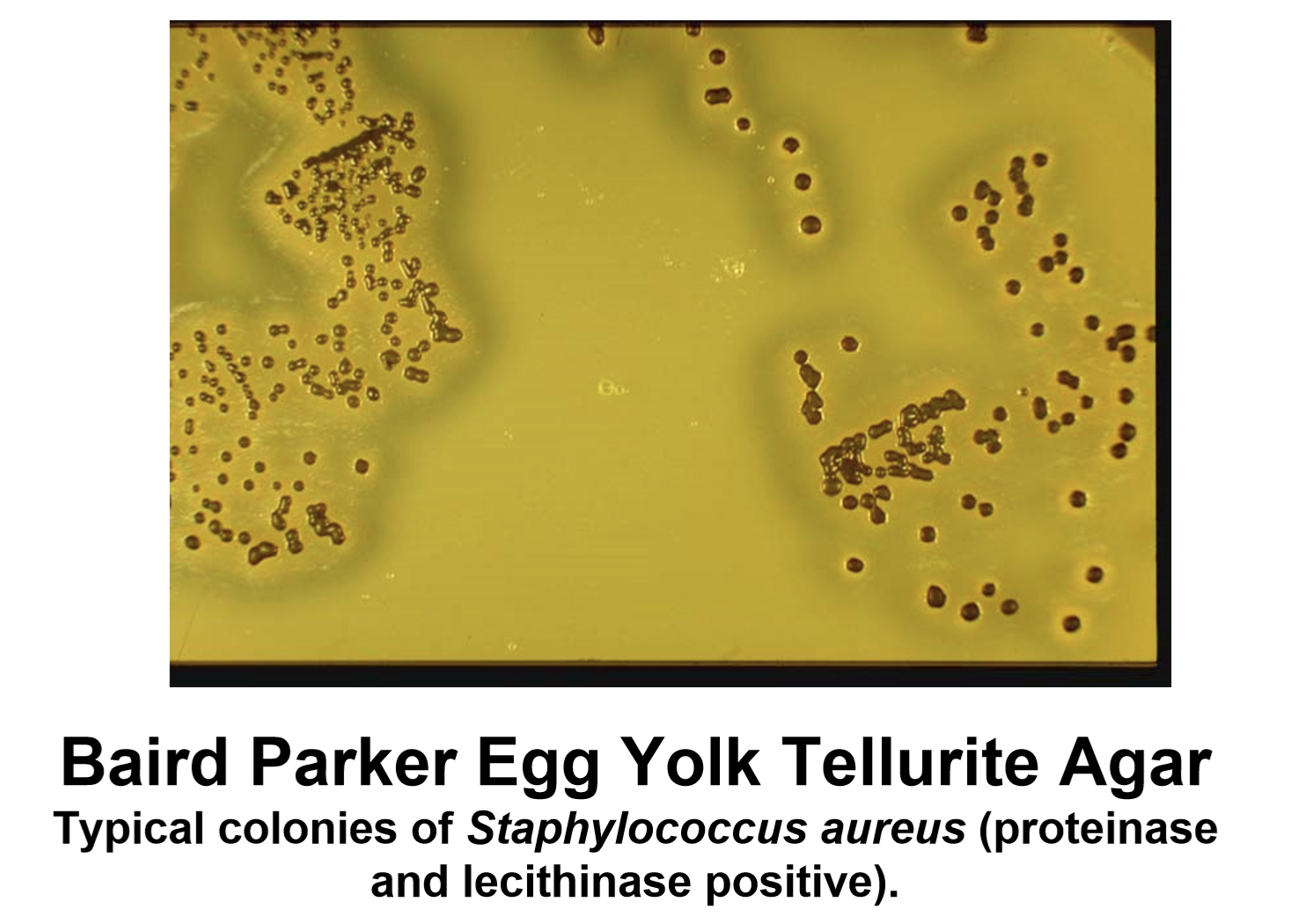
Baird Parker Base Agar supplemented with egg yolk tellurite emulsion is recommended by ISO 6888-1 for the isolation and enumeration of S. aureus in food and animal feed.
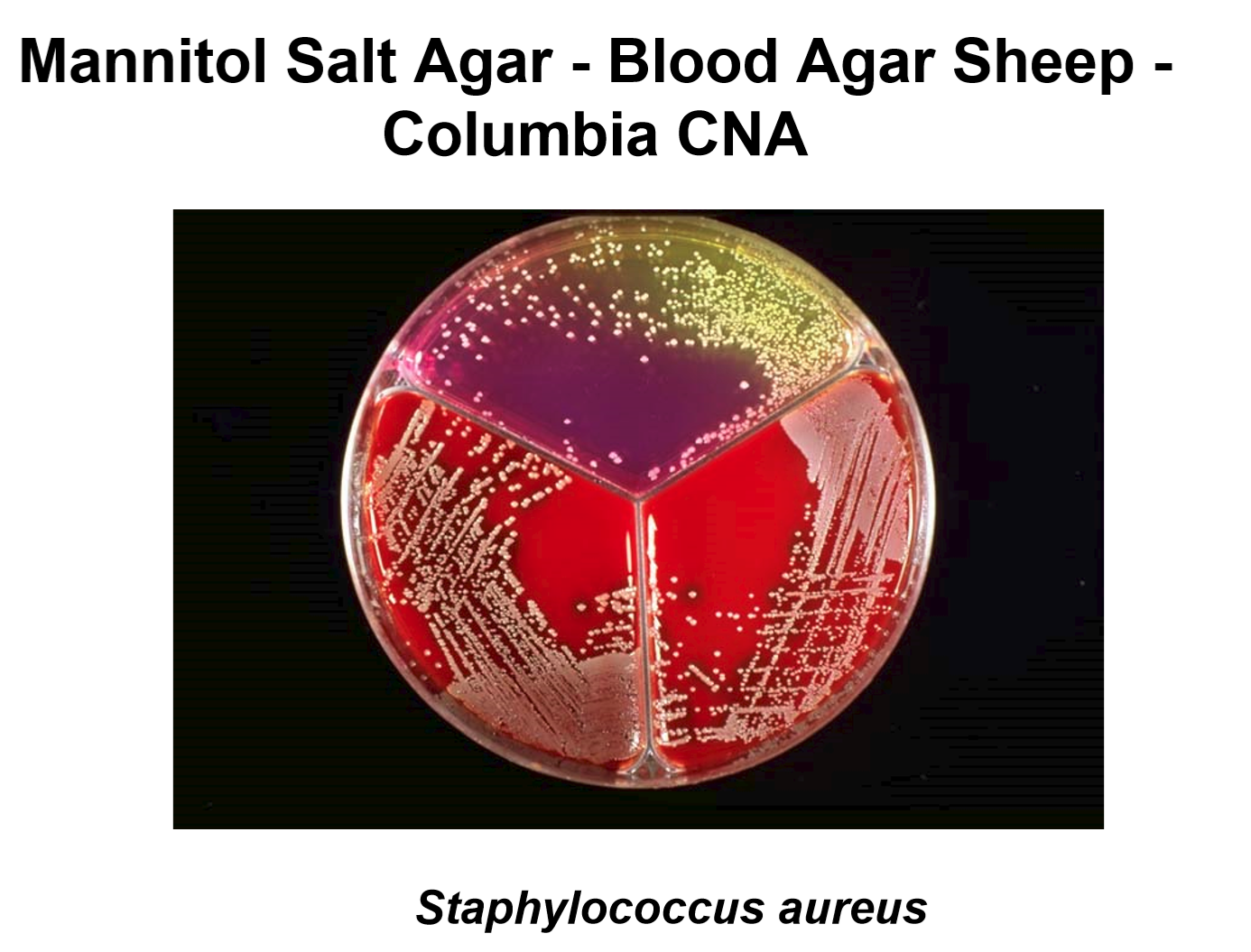
Blood Sheep Agar is a multipurpose agar for many cocci including staphylococcus. Columbia Blood Agar is formulated according to Columbia University who discovered that a combination of meat and casein peptones gave better results than sheep blood agar. It allows more abundant and rapid growth of cocci. Columbia CNA agar is formulated with the addition of colistin and nalidixic acid to inhibit the growth of gram-negative bacteria. Mannitol Agar is for the presumptive identification of pathogenic staphylococci. It contains a high content of salt which inhibits the growth of most bacteria except staph spp. Presumptive pathogenic staph colonies grow in large colonies surrounded by yellow halos whilst non pathogenic ones grow less luxuriously forming small colonies surrounded by purple halos.

MC Media Pads Staphylococcus Aureus Incubation: 35 °C, 24 hours. S. aureus form circular light blue/ blue colored colonies. Even though other bacteria are inhibited strongly, some bacteria (especially Bacillus species) can form gray/ black colored colonies.
Testing for staphylococcus enterotoxin

Staphylococcus enterotoxin
Enterotoxin produced by staphylococcus aureus causes food poisoning and toxic shock syndrome. There are more than 20 staphylococcal enterotoxins but the most common ones are A, B, C, D, and E. These toxins are highly resistant to denaturation and are recognized as heat resistant. The incubation time is 2hr 45mins. The test format is a sandwich immunoassay in 96 well trays. The limit of detection is 0.25ng (liquid), 0.375ng (solids) and 0.25ng (bacterial supernatant).
LEARN MORE
Reach Us Today

We provide the best services about science.
About Company
Sitemap
Please contact our friendly sales staff for more information.
Feel free to ask us questions. We would love to assist you !
